Table of Contents
Overview
The Ultrasound Module provides a microservice based API for ultrasound devices. The main features are:
- Microservice-enabled life cycle management, allowing other modules to easily consume mitk::USDevice-functionality.
-
Handling and processing of ultrasound image data.
- Fast image preprocessing capabilities (gray scale conversion, cropping) via OpenCV.
- Advanced image processing functions via mitk filters.
- The mitk::USVideoDevice class allows to connect any ultrasound device with a video-out via a frame grabber.
-
Connection of API-Enabled devices (specifically the Telemed LogicScan 128 is implemented).
- The submodule USHardwareTelemed provides classes for handling a Telemed API device (mitk::USTelemedDevice).
- Control of API-enabled Devices via MITK (Widgets for basic B mode controls and probe selection are available).
- Designed to interact with the IGT Module for tracking functionality.
This module requires OpenCV to be enabled in the superbuild options via CMake. Its functionality is made available to the user via the UltrasoundSupport plugin
Documentation on how to use Telemed API devices can be found on Controlling API Devices of Telemed.
Ultrasound Device Hierarchy
Ultrasound Devices are managed in a simple hierarchy:
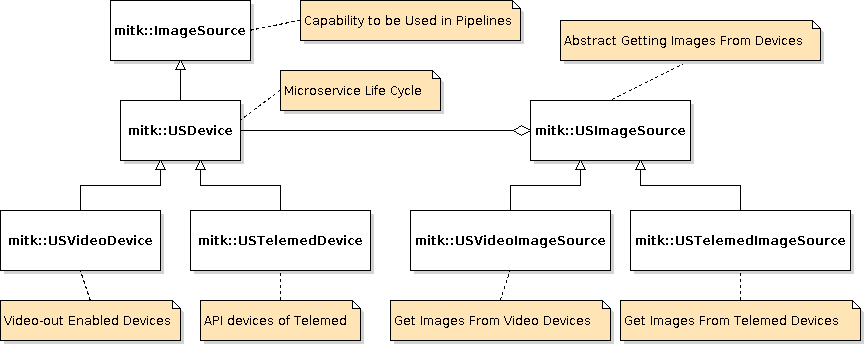
- mitk::USDevice: The common superclass for all ultrasound devices. Deriving from this class will make sure that US-specific GUI-Components will be able to interact with your class. Especially, the microservice life cycle is modeled in this class.
- mitk::USImageSource: Abstract class used by the mitk::USDevice for getting the images from the ultrasound device. The images are filtered by one ore more mitk::AbstractOpenCVImageFilter if they were set to the mitk::USImageSource object. Each concrete subclass of mitk::USDevice has to subclass mitk::USImageSource to handle the actual receiving of images from the ultrasound device.
-
Two devices are implemented in the ultrasound module:
- mitk::USVideoDevice: This class can be used for every ultrasound device that is connected to the PC via a frame grabber or a similar video input device. The UltrasoundSupport plugin enables the user to create instances of mitk::USVideoDevice. There also is a reusable Widget for this Task in the USUI Module.
- mitk::USTelemedDevice: This class can be used for API-enabled ultrasound devices of Telemed (e.g. Telemed LogicScan 128).
- One can add another device by subclassing mitk::USDevice and mitk::USImageSource. Additionally the control interfaces may be implemented (see USControlInterfaces ).
Ultrasound Device Life Cycle
Each mitk::USDevice follows a life cycle handling the availabilty as a micro service and the connection to the hardware:
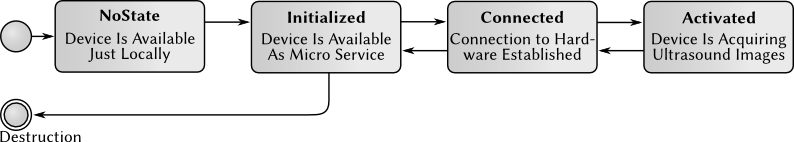
For changing the states corresponding methods are available in mitk::USDevice: mitk::USDevice::Initialize() for initialization, mitk::USDevice::Connect() for connecting, mitk::USDevice::Disconnect() for disconnecting and so on. For example, once an object of mitk::USDevice is constructed it can be made available as a micro service via a call to mitk::USDevice::Initialize(). The state changes to Initialized then and the device is available to other modules or plugins (UltrasoundSupport , QmitkUSDeviceManagerWidget) through the micro service framework.
The methods for changing the states should not be overwritten by sublcasses. Instead mitk::USDevice::OnInitialization(), mitk::USDevice::OnConnection() and so on can be overwritten for handling everything that has to be done on the corresponding state change.
When the mitk::USDevice object was created at first it is available just locally. An initialized device is available as a micro service, but not connected to the real hardware. A connected device is connected to the hardware, but no acquiring images. Finally, an activated device is acquiring images from the ultrasound hardware.
Control Interfaces for API Devices
Capabilities of API-based ultrasound devices are available through control interfaces which are shown below:
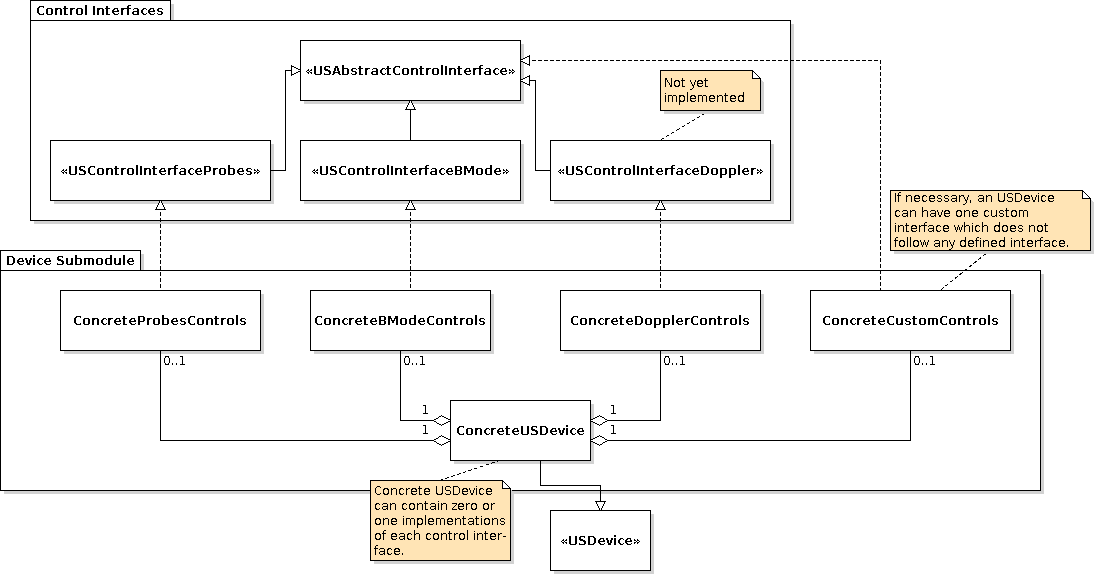
The control interfaces mitk::USControlInterfaceProbes and mitk::USControlInterfaceBMode are available, while mitk::USControlInterfaceDoppler is empty at the moment. Every sublcass of mitk::USDevice can use an implementation of each of these interfaces, but this is not necessary. The mitk::USVideoDevice for example uses a custom control interface only (mitk::USVideoDeviceCustomControls), which is a subclass of mitk::USAbstractControlInterface. The mitk::USTelemedDevice uses mitk::USTelemedBModeControls for handling the ultrasound b mode and mitk::USTelemedProbesControls for handling the connected ultrasound probe.
Each custom control interface needs its own Widget (subclassed of QmitkUSAbstractCustomWidget), if it should be possible to control its functionality by using the UltrasoundSupport plugin. For the standard interfaces mitk::USControlInterfaceProbes, mitk::USControlInterfaceBMode and mitk::USControlInterfaceDoppler there are Widgets available in the USUI module (QmitkUSControlsProbesWidget, QmitkUSControlsBModeWidget, QmitkUSControlsDopplerWidget) which can be used by plugins. For each Widget an object of the corresponding control interface must be set on its constructor call. A class diagram showing how the Widgets are connected to the control interfaces can be seen below:
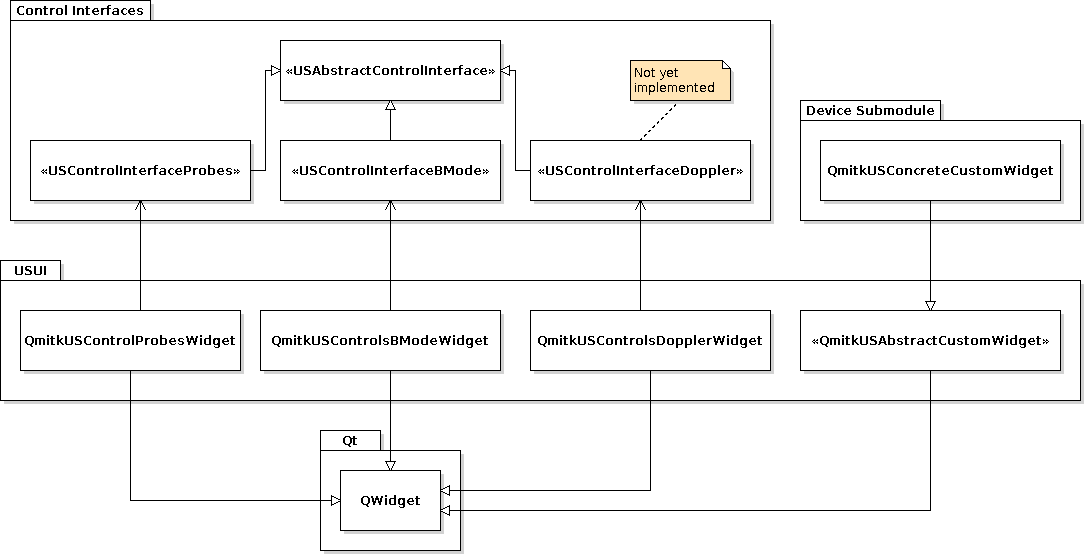
A plugin can use the Widgets by creating a new object of the Widget and setting the corresponding interface object of the mitk::USDevice which should be controlled. How to use custom widgets is described in the class documentation of QmitkUSAbstractCustomWidget.
Available Widgets
There are some Widgets available in the USUI module that can be used for plugin development: a device management Widget, a Widget for creating new mitk::USVideoDevice objects and widgets for the control interfaces of API device. The usage of the Widgets is described in more detail in the UltrasoundSupport Plugin Documentation.
QmitkUSDeviceManagerWidget
The QmitkUSDeviceManagerWidget can view every connected mitk::USDevice and allows the user to activate and deactivate devices. Additionally mitk::USVideoDevice can be created using the QmitkUSNewVideoDeviceWidget and removed by a corresponding button.
QmitkUSNewVideoDeviceWidget
The QmitkUSNewVideoDeviceWidget allows the user to configure a frame grabber or other video input as a mitk::USVideoDevice.
Control Interface Widgets
There exists several widgets for controling ultrasound devices: QmitkUSControlsBModeWidget, QmitkUSControlsProbesWidget, QmitkUSControlsCustomVideoDeviceWidget. Own custom control widgets can be added by subclassing the available QmitkUSAbstractCustomWidget.
