Table of Contents
Selecting data nodes is frequently done when working with the MITK workbench. Most of the views in MITK require one or more selected data nodes that will be somehow processed by the underlying algorithms, such as image segmentation, image registration, basic image processing, image statistics computation etc.. In order to overcome some disadvantages of the old data node selection concept, the following new selection concept has been implemented.
This page introduces the concept and the corresponding implementation. The document starts with a brief explanation of the disadvantages of the old concepts and justifies a need for the new concept.
Migration idea / background
The old data node selection concept is a mixture of a global and a local selection concept:
Global selection
The global selection was realized by the data manager view: Selecting one or more data nodes in the data manager view lead to a propagation of the selected nodes via the blueberry framework. Other views that derive from QmitkAbstractView received the new selection and processed it individually. All activated views were able to receive the new selection successively, thus it is called a global selection.
Local selection
The local selection was realized by Qt elements inside a view. An example of such an element is the QmitkDataStorageComboBox. This combo box contains the nodes from the data storage and allows to select one of it. A combo box can be included in a view multiple times. Additionally a node predicate can be set for a combo box so that only a filtered subset of all nodes in the data storage is contained in the combo box. A selection inside a combo box does not affect the selection of another combo box (in the same or another view), thus it is called a local selection.
Both concepts have reached their functional limit:
- the global selection does not offer the functionality to filter data nodes
- the global selection does not allow to select different data nodes in different views
- the selection order for multi-node selection might be important, which can be cumbersome to achieve via the data manager
- the local selection does not offer enough flexibility:
- it does not allow to propagate data node selections
- it does not allow multi node selection (multiple combo boxes are needed)
- it does not show the visibility / hierarchy of the data nodes
The latest trend was to change the design of the view of the MITK workbench so that the local concept (using the QmitkDataStorageComboBox) was used wherever possible. This was done since the problems of the global selection concept where severe. In cases where the local concept was used positive feedback was received.
New selection concept
The new selection concept is based on the idea of a local selection concept. This accounts for some fundamental requirements, such as individual data node selection for each view and data node filtering. Furthermore it clearly defines the responsibility of the data manager view: the data manager is only used to manage the data to render, e.g. defining the node hierarchy (rendering order) or setting the color or transparency of the pixel data.
Additionally the new local selection concept is also able to overcome the problems of the previous local concept: It allows data node selection propagation, multi node selection and is able to show additional information such as data node hierarchy or node visibility. How this is achieved will be explained in the following sections.
Basic idea
The basic idea is to provide a set of classes that define the basic functionality of the new selection concept. These classes allow the use of existing and the development of new data storage inspectors or node selection widgets.
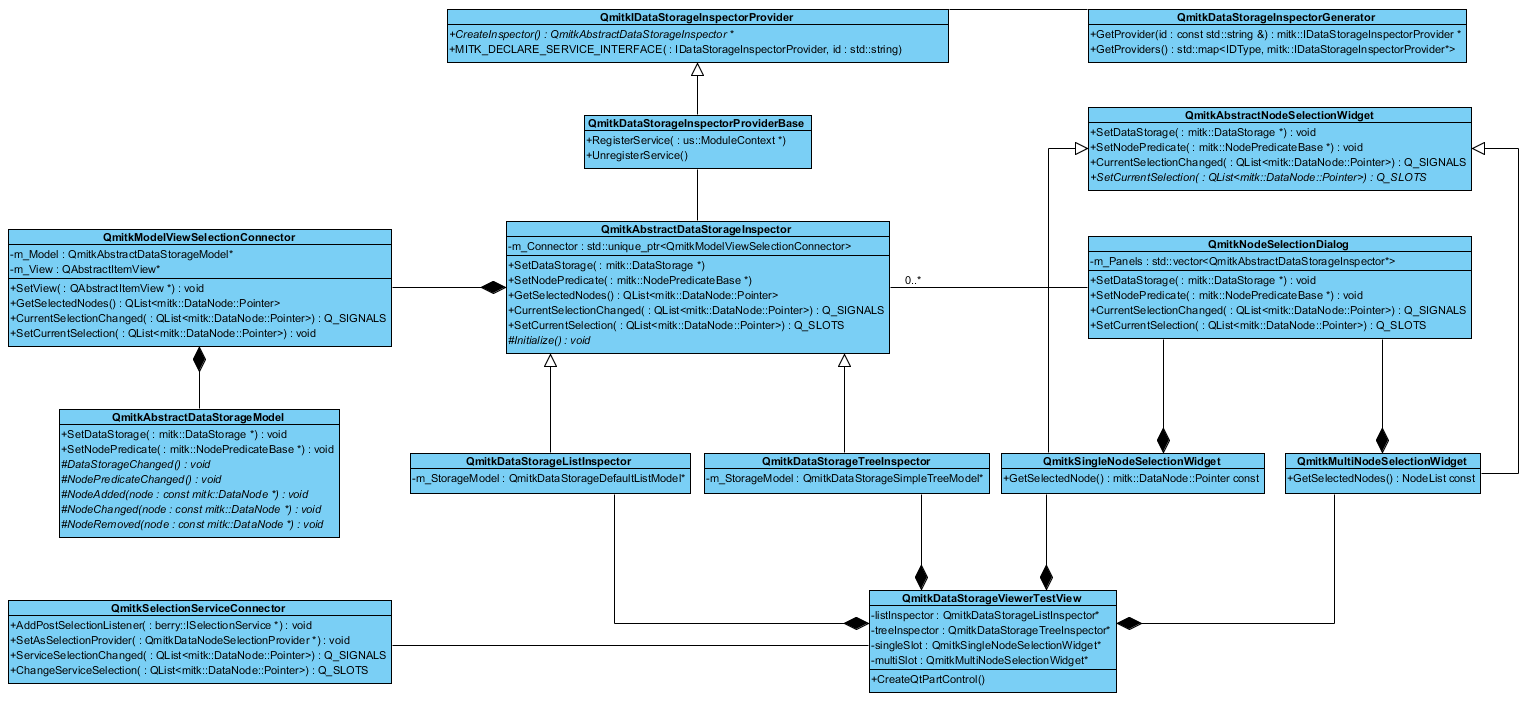
Included in this concept is a set of basic data storage inspectors and node selection widgets that are frequently needed. A developer can extend these classes to create own data storage inspectors or node selection widgets to customize a plugins behavior and design.
The following paragraphs further describe the most important classes:
The QmitkAbstractDataStorageModel extends the QAbstractItemModel to provide a custom item model for the data storage. This custom item model extends the Qt-model functionality in order to accept an mitk::DataStorage and an mitk::NodePredicateBase.
The data storage is used to define on which data storage the model operates. In order to update the data storage model if the data storage changes, the QmitkAbstractDataStorageModel provides four pure virtual functions, QAbstractItemModel::DataStorageChanged, QAbstractItemModel::NodeAdded, QAbstractItemModel::NodeChanged and QAbstractItemModel::NodeRemoved. This abstract model calls the first function if the data storage has been reset using the SetDataStorage-function (i.e. to a new data storage or to a nullptr). The last three functions are connected to the corresponding events of the data storage (AddNodeEvent, ChangedNodeEvent and RemoveNodeEvent).
The node predicate can be set and used to filter the data storage, so that only a subset of the contained data nodes is represented by the data storage model. In order to update the data storage model if the node predicate changes, the QmitkAbstractDataStorageModel provides a pure virtual function, QAbstractItemModel::NodePredicateChanged. This abstract model calls this function if the node predicate has been reset using the SetNodePredicate-function (i.e. to a new node predicate or to a nullptr).
Any subclass of this abstract data storage model can define its own functionality by overriding the five corresponding functions. The abstract data storage model does not implement any Qt model functionality, so the functions of the QAbstractItemModel have to be overwritten in the subclasses, according to the model type (e.g. list model, table model).
QmitkAbstractDataStorageInspector
The QmitkAbstractDataStorageInspector serves as a base class that can be derived from to provide a custom view onto the data storage using a QmitkAbstractDataStorageModel derivative. This custom widget extends the QWidget functionality in order to accept an mitk::DataStorage and an mitk::NodePredicateBase. The data storage is used to define which data storage the widget should inspect. The node predicate can be set and later be used to filter the data storage, so that only a subset of the contained data nodes is inspected by the data storage inspector. The data storage and the node predicate can be set by the corresponding setter, which in turn calls the pure virtual function QmitkAbstractDataStorageInspector::Initialize. Any subclass of this abstract data storage inspector can now define its own functionality inside the Initialize-function to define what happens if the data storage or the node predicate is (re-)set. Typically an inspector will forward the data storage and the node predicate to the data storage model to make it aware of the data it should hold.
Additionally a data storage inspector holds a QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector and initializes it with a QAbstractItemView derived class (e.g. a QListView) and the data storage model. The idea behind this connector-class will be explained in the next section.
Furthermore the abstract class provides a QSignal, CurrentSelectionChanged(NodeList), that is emitted if the selection of the underlying data storage model has changed. The abstract class also provides two QSlots, SetSelectOnlyVisibleNodes(bool) and SetCurrentSelection(NodeList). Calling these slots will forward the given arguments to the model view selection connector member which in turn can manipulate the data storage models selection.
QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector
The QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector is used to transform a model selection into a list of selected data nodes and vice versa. The class accepts a QAbstractItemView with a corresponding QmitkAbstractDataStorageModel that operates on a data storage.
The connector class provides a QSlot, QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector::ChangeModelSelection(const QItemSelection&, const QItemSelection&) that is called if the selectionChanged-signal of the selection model of the given QAbstractItemView is emitted. This indicates a change in the model selection. The slot itself will emit a QSignal, QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector::CurrentSelectionChanged(QList<mitk::DataNode::Pointer>), where the selection of the item view has been transformed to a list of selected data nodes. The transformation is done by using the member functions QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector::GetSelectedNodes and QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector::GetInternalSelectedNodes: The selected indices of the item view's selection model are used to receive the corresponding data node from the data storage model.
Additionally the connector class provides a function QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector::SetCurrentSelection(QList<mitk::DataNode::Pointer>), which can be used to change the selection of the QAbstractItemView from outside of this class. The nodes of the list are compared to the nodes that are valid for the data storage model, according to the current node predicate. If the given nodes are valid the corresponding indices are selected in the view. If the given list is equal to the current selection, nothing happens.
Using the QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector::SetSelectOnlyVisibleNodes(bool selectOnlyVisibleNodes) function it is possible to set a variable that defines if only those nodes should be de-/selectable that are included in the list of filtered data nodes. This means that a new selection ca be received, which might change the current selection of the view. However, those nodes that are not visible, as defined by the node predicate of the data storage model, will not be de-/selectable.
QmitkSelectionServiceConnector
The QmitkSelectionServiceConnector is used to interact with the global selection bus: It provides a private QSlot, QmitkSelectionServiceConnector::OnServiceSelectionChanged(const berry::IWorkbenchPart::Pointer&, const berry::ISelection::ConstPointer&), which is internally called if the selection of the selection bus has been changed. This slot transforms the berry selection into a list of selected data nodes and emits the QSignal QmitkSelectionServiceConnector::ServiceSelectionChanged(QList<mitk::DataNode::Pointer>). Typically this signal is used to react in another class on the change of selected nodes from the selection bus, e.g. inside the QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector to change the selection of an item view via the selection bus.
Additionally the connector class provides a function, QmitkSelectionServiceConnector::SetAsSelectionProvider(QmitkDataNodeSelectionProvider*), which can be used to set the connector as a provider for data node selections that will be sent via the global selection bus. This way a QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector can propagate its selection to all listeners of the selection bus via the QmitkSelectionServiceConnector. The following code shows how the two connector classes can be connected:
The data storage inspectors
The QmitkNodeSelectionDialog is the main widget to be used in order to select data nodes from the data storage. It is a pop-up-dialog that can be included in any other widget, such as the QmitkSingleNodeSelectionWidget or the QmitkMultiNodeSelectionWidget.
The node selection dialog serves as a container for different QmitkAbstractDataStorageInspector: It uses a QTabWidget that holds the different data storage inspectors. These inspectors are received by using the mitk::DataStorageInspectorGenerator class. Each data storage inspector is then added to the tab widget and its CurrentSelectionChanged-signal is connected to the dialog's OnSelectionChanged-slot. If the selection inside a data storage inspector changes, the slot sets the selected nodes of the dialog and propagates this selection to all its known data storage inspectors. This way all inspectors that are currently held in the tab widget show the same selection.
In order to dynamically add and receive new data storage inspectors the microservice approach is used: Each concrete implementation of a data storage inspector provider registers itself as an mitk::IDataStorageInspectorProvider via the service registry. For this the QmitkDataStorageInspectorProviderBase can be used. Any class can use the mitk::DataStorageInspectorGenerator to either receive all registered data storage inspector providers or a specific one. A provider in turn provides a specific data storage inspector, which can be used to display the data nodes of the data storage.
The user can define which of the registered data storage inspectors should be available when using a QmitkNodeSelectionDialog: Using the workbench preferences one can select the Node Selection entry and enable or disable certain data storage inspectors.
mitk::IDataStorageInspectorProvider
The mitk::IDataStorageInspectorProvider declares the service interface for all data storage inspector providers. It must be implemented to override the mitk::IDataStorageInspectorProvider::CreateInspector-function. This function should return the concrete data storage inspector created by the provider. In order to simplify the use of this interface and to add some basic functionality, the QmitkDataStorageInspectorProviderBase class should be used.
QmitkDataStorageInspectorProviderBase
The QmitkDataStorageInspectorProviderBase implements the mitk::IDataStorageInspectorProvider-interface and is a template implementation: It can be used with a concrete implementation of the QmitkAbstractDataStorageInspector; the data storage inspector that the provider base should create. When the provider base is initialized it registers itself as an mitk::IDataStorageInspectorProvider service reference. The provider base overrides the mitk::IDataStorageInspectorProvider::CreateInspector-function of the interface to create and return a concrete instance of the provided data storage inspector. This way each concrete data storage inspector can be created by receiving the corresponding data storage inspector provider as a service and using the mitk::IDataStorageInspectorProvider::CreateInspector-function.
mitk::DataStorageInspectorGenerator
The mitk::DataStorageInspectorGenerator simply provides two static functions to receive all or a specific data storage provider. These providers have been registered before as an mitk::IDataStorageInspectorProvider service. Using the microservice approach the provider can be received without any further knowledge about the concrete provider. This way a developer can easily add their own concrete data storage inspector by creating a new QmitkDataStorageInspectorProviderBase with the concrete inspector as the template argument.
Adding a custom data storage inspector
As mentioned above, the microservice approach is used inside the mitk::DataStorageInspectorGenerator to receive all known or a specific data storage provider. In order to let the microservice know about a new custom data storage inspector, it has to be provided by a data storage provider. This data storage provider has to be registered as an mitk::IDataStorageInspectorProvider service. The new selection concept provides the QmitkDataStorageInspectorProviderBase class (see above), which automatically registers the data storage provider as a provider service. For this the following constructor can be used:
The constructor can be used like this:
This registers a new QmitkDataStorageInspectorProviderBase instance as an mitk::IDataStorageInspectorProvider service. The data storage provider and its specific data storage inspector can later be received using the following code:
In the code snippets the QmitkDataStorageListInspector class was used. This is an example of a concrete data storage inspector which is provided by the presented selection concept. It is a frequently used data storage inspector and already registered via a corresponding provider base. This is done inside the mitk::QtWidgetsActivator class; a class that is used during module activation. Currently four frequently used custom data storage inspectors are already registered. The following sections describe these four frequently used basic inspectors.
QmitkDataStorageListInspector
The QmitkDataStorageListInspector is an example of a concrete data storage inspector, subclassing the QmitkAbstractDataStorageInspector. Its only purpose is to provide a custom model-view pair that represents a list view onto the data storage. The view is a simple QListView. The model is a custom model derived from the above mentioned QmitkAbstractDataStorageModel: The QmitkDataStorageDefaultListModel overrides the five pure virtual functions to react on changes of the data storage or the node predicate: each function calls the private UpdateModelData-function, which will simply retrieve the currently available (possibly filtered) data nodes of the data storage. Additionally the default list model needs to override some functions of the QAbstractItemModel in order to represent a list model. One important function to override is the data(const QModelIndex& index, int role = Qt::DisplayRole)}-function: This function is used by Qt to define what has to be displayed in the list view. It is important that a custom model returns an mitk::DataNode::Pointer object for a model index when the role is mitkDataNodeRole.
QmitkDataStorageTreeInspector
The QmitkDataStorageTreeInspector is another example of a concrete data storage inspector, subclassing the QmitkAbstractDataStorageInspector. Its only purpose is to provide a custom model-view pair that represents a tree view onto the data storage. The view is a simple QTreeView. The model is a custom model derived from the above mentioned QmitkAbstractDataStorageModel: The QmitkDataStorageSimpleTreeModel needs to override some functions of the QAbstractItemModel in order to represent a tree model. Again, one important function to override is the data(const QModelIndex& index, int role = Qt::DisplayRole)}-function. It is important that the simple tree model returns an mitk::DataNode::Pointer object for a model index when the role is mitkDataNodeRole. The QmitkDataStorageTreeInspector is designed to reflect the classical data manager view.
QmitkDataStorageSelectionHistoryInspector
The QmitkDataStorageSelectionHistoryInspector is a concrete data storage inspector that allows to view the recently used nodes of the data storage. It uses the same QmitkDataStorageDefaultListModel as the QmitkDataStorageListInspector. The QmitkDataStorageSelectionHistoryInspector provides a function to add nodes to the selection history. The selection history will be displayed in chronological order and a selected node will only appear once in the history list.
QmitkDataStorageFavoriteNodesInspector
The QmitkDataStorageFavoriteNodesInspector is a concrete data storage inspector that allows to view a user's favorite nodes of the data storage. It extends the QmitkDataStorageListInspector. The QmitkNodeSelectionDialog provides a function to set nodes as favorite nodes using a specific node property. It allows the QmitkDataStorageFavoriteNodesInspector to use a customized node predicate to filter nodes according to their favorite-property-state. This favorite-property-state is defined by the node property "org.mitk.selection.favorite" The QmitkDataStorageFavoriteNodesInspector provides a function to unset nodes as favorite nodes by setting this specific node property to "false", so that they won't appear anymore in the list of favorite nodes.
The node selection widgets
QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget
The QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget extends the QWidget to provide a custom widget to show data nodes after they have been selected using the QmitkNodeSelectionDialog with its data storage inspectors. This custom widget extends the QWidget functionality in order to accept an mitk::DataStorage and an mitk::NodePredicateBase. The data storage is used to define which data storage should be used by the selection dialog. The node predicate is used to filter the data storage. Any subclass of this abstract node selection widget needs to override the following functions in order to customize its behavior:
- void QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget::SetCurrentSelection(NodeList), in order to set the selection of this widget given an external list of selected nodes. This function may be customized to filter the incoming selected nodes.
- void QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget::UpdateInfo(), in order to set the information text and enable / disable the control buttons according to the current selection.
- void QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget::OnNodePredicateChanged(), in order to react to a change of the used node predicate. Changing the node predicate might alter the selection. This function is called if QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget::SetNodePredicate(mitk::NodePredicateBase*) was called.
- void QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget::OnDataStorageChanged(), in order to react to a change of the used data storage. Changing the data storage might alter the selection. This function is called if QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget::SetDataStorage(mitk::DataStorage*) was called.
Furthermore QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget::SetSelectOnlyVisibleNodes(bool selectOnlyVisibleNodes) can be overridden to set the modus to (not) include invisible nodes in the selection. Default value is true.
QmitkSingleNodeSelectionWidget
The QmitkSingleNodeSelectionWidget is an example of a concrete node selection widget, subclassing the QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget. It overrides the virtual functions to react on changes of the node selection. If the QmitkNodeSelectionButton of the widget is pressed, a QmitkNodeSelectionDialog is opened as a pop-up for data node selection. This dialog is a QmitkNodeSelectionDialog (see The data storage inspectors). It presents the currently known and active data storage inspectors for the user to select a single data node. If a selection is confirmed, the pop-up closes and the selected data node will be shown in the QmitkSingleNodeSelectionWidget. The user will see a thumbnail or an icon of the data node (if available) along with an HTML text of the data node info.
The QmitkSingleNodeSelectionWidget is currently used inside plugin views to allow to select specific nodes of the data storage for further processing. A plugin view can connect a function to the CurrentSelectionChanged-signal to immediately react on a new selection of the QmitkSingleNodeSelectionWidget. Using QmitkSingleNodeSelectionWidget::GetSelectedNode the currently selected node of the selection widget can be retrieved anytime.
Additionally an auto-selection-mode is available that automatically selects a node from the data storage if such a data storage is set and contains a node that matches the given predicate. The auto-selection-mode only works if the QmitkSingleNodeSelectionWidget does not already show a selected node.
The QmitkMultiNodeSelectionWidget is another example of a concrete node selection widget, subclassing the QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget. It overrides the virtual functions to react on changes of the node selection. If the 'Change selection'-button is pressed a QmitkNodeSelectionDialog is opened as a pop-up for data node selection. This dialog is a QmitkNodeSelectionDialog (see The data storage inspectors). It presents the currently known and active data storage inspectors for the user to select a single data node. If a selection is confirmed, the pop-up closes and the selected data nodes will be shown in the QmitkMultiNodeSelectionWidget. Unlike single node selection the multi node selection is presented as a list of all the selected nodes.
The QmitkMultiNodeSelectionWidget is currently used inside plugin views to allow to select a set of specific nodes of the data storage for further processing. A plugin view can connect a function to the CurrentSelectionChanged-signal to immediately react on a new selection of the QmitkMultiNodeSelectionWidget. Using QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget::GetSelectedNodes the currently selected node of the selection widget can be retrieved anytime.
QmitkMultiNodeSelectionWidget::SetSelectionCheckFunction allows to define a function that puts a constraint on the node selection (dialog) to only allow specific combinations or selections of nodes. The result of the constraint check has to be either an empty string (indicating a valid node selection) or a string that explains the error / constraint violation. A simple check function can look like this:
This check function will be passed to the QmitkNodeSelectionDialog and is used to print an error message, if an invalid selection is made inside the node selection dialog. This will prevent the user from confirming an even selection. If a valid selection is made no error message will be printed and the user can confirm the selection.
The QmitkNodeSelectionButton is a customized QPushButton and is used for example inside the QmitkSingleNodeSelectionWidget: It displays the thumbnail or icon of the selected data node (if available) along with an HTML text of the data node info.
The DataStorageViewerTest plugin
The org.mitk.gui.qt.datastorageviewertest plugin can be enabled and used inside the MITK workbench. It serves as a test / demo plugin with a single view that shows different uses of the new selection concept and its related classes. The following classes are used:
- Top row: A QmitkDataStorageListInspector
- Top right: A QmitkDataStorageTreeInspector
- Bottom left: A QmitkSingleNodeSelectionWidget
- Bottom right: A QmitkMultiNodeSelectionWidget
The top row presents the two examples of an implementation of the QmitkAbstractDataStorageInspector. They display the whole content of the given data storage in two different ways. No node predicates are used in this case. Both inspectors come with two checkboxes to set each inspectors as a selection provider and a selection listener. With these checkboxes turned on the QmitkSelectionServiceConnector for each inspector is connected to the QmitkModelViewSelectionConnector of each inspector (as shown in QmitkSelectionServiceConnector).
See how the selection also changes in the inspectors if nodes are selected in the mitk::DataManager and the Set as selection listener-checkbox is checked for the inspector.
The bottom row presents the two examples of an implementation of the QmitkAbstractNodeSelectionWidget: They display a specific data node selection that was made by the user. Both widgets come with several checkboxes to modify the behavior of the selection widgets.
