Table of Contents
This page will give you an overview of creating your own command line tool that can be integrated into a MiniApp.
What's a MiniApp command line tool?
A MiniApp command line tool allows for configuration of command line arguments and eases the access to these argument values. Additionally, a command line tool provides a XML representation of the configured arguments. This XML representation can be used for automatic user interface generation.
Setting up a command line tool
This section describes the most important code parts of a command line tool using the ExampleToUpperCaseMiniApp.cpp as an example. See How to create a new MITK Module for a suggested structure of a new module and its MiniApps.
Each MiniApp contains its own main function.
Within the main function the first thing should be to configure the accepted arguments. This can be done using the mitkCommandLineParser.
Our example accepts an input filename an output filename and an optional flag for verbose processing.
Following argument types are available for the addArgument method:
- String
- Bool
- StringList
- Int
- Float
- InputDirectory
- InputFile
- InputImage
- OutputDirectory
- OutputFile
The distinction between InputFile/OutputFile and InputDirectory/OutputDirectory respectively ensures that the appropriate UI widget is chosen. The label string passed to the addArgument method is the label for the corresponding UI widget.
After specification of allowed arguments the parser's parseArguments method is called.
After all arguments have been parsed we can do the actual processing. In this case we read the file, convert the contained text to upper case and write the new data to the specified output location.
Example Help Output
Running the ExampleToUpperCaseMiniApp without an argument or with wrong ones:
... will emit the following help text:
Command Line Utility *To Upper Case* in Category *MITK-Examples* An example MiniApp that converts the contents of a test file to upper case. German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) Use --xml to generate an XML description parsable as a CTK Command Line Module Plugin. Optional parameters -v, --verbose, Whether to produce verbose output (optional) Required I/O parameters -i, --input, input file (.txt/.example) -o, --output, where to save the output (.txt/.example)
Retrieving XML argument description
According to the specified command line arguments, a XML representation of the arguments is generated and emitted on the console if the MiniApp command line tool is executed with argument "--xml".
In order to use the XML representation for automatic user interface generation additional information has to be provided for the parser. Please provide category, title, description and contributor as shown in code snippet below:
Note that in the generated UI the parameter widgets are contained in a group box. There is a default label ("Parameters") and a default description ("Groupbox containing parameters.") specified. The label of such a parameter group and the description can be set via the parser's changeParameterGroup method. The method must be called before adding the arguments.
Example XML Output
Running the ExampleToUpperCaseMiniApp with argument "--xml" ...
... will emit following XML description:
<executable>
<category>MITK-Examples</category>
<title>To Upper Case</title>
<description>An example MiniApp that converts the contents of a test file to upper case.</description>
<contributor>German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ)</contributor>
<parameters>
<label>Parameters</label>
<description>Parameters</description>
<file>
<name>input</name>
<description>input file (.txt/.example)</description>
<label>Input file</label>
<longflag>input</longflag>
<flag>i</flag>
<channel>input</channel>
</file>
<file>
<name>output</name>
<description>where to save the output (.txt/.example)</description>
<label>Output file</label>
<longflag>output</longflag>
<flag>o</flag>
<channel>output</channel>
</file>
<boolean>
<name>verbose</name>
<description>Whether to produce verbose output</description>
<label>Verbose Output</label>
<longflag>verbose</longflag>
<flag>v</flag>
</boolean>
</parameters>
</executable>
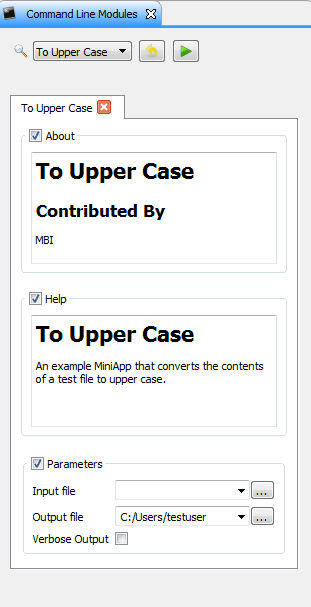
This XML description is used for automatic user interface generation in MITK Workbench. The generated user interface is depicted in the following screenshot: