|
Medical Imaging Interaction Toolkit
2016.11.0
Medical Imaging Interaction Toolkit
|
|
Medical Imaging Interaction Toolkit
2016.11.0
Medical Imaging Interaction Toolkit
|
The tensor reconstruction view allows ITK based tensor reconstruction [3]. The advanced settings for ITK reconstruction let you configure a manual threshold on the non-diffusion weighted image. All voxels below this threshold will not be reconstructed and left blank. It is also possible to check for negative eigenvalues. The according voxels are also left blank.
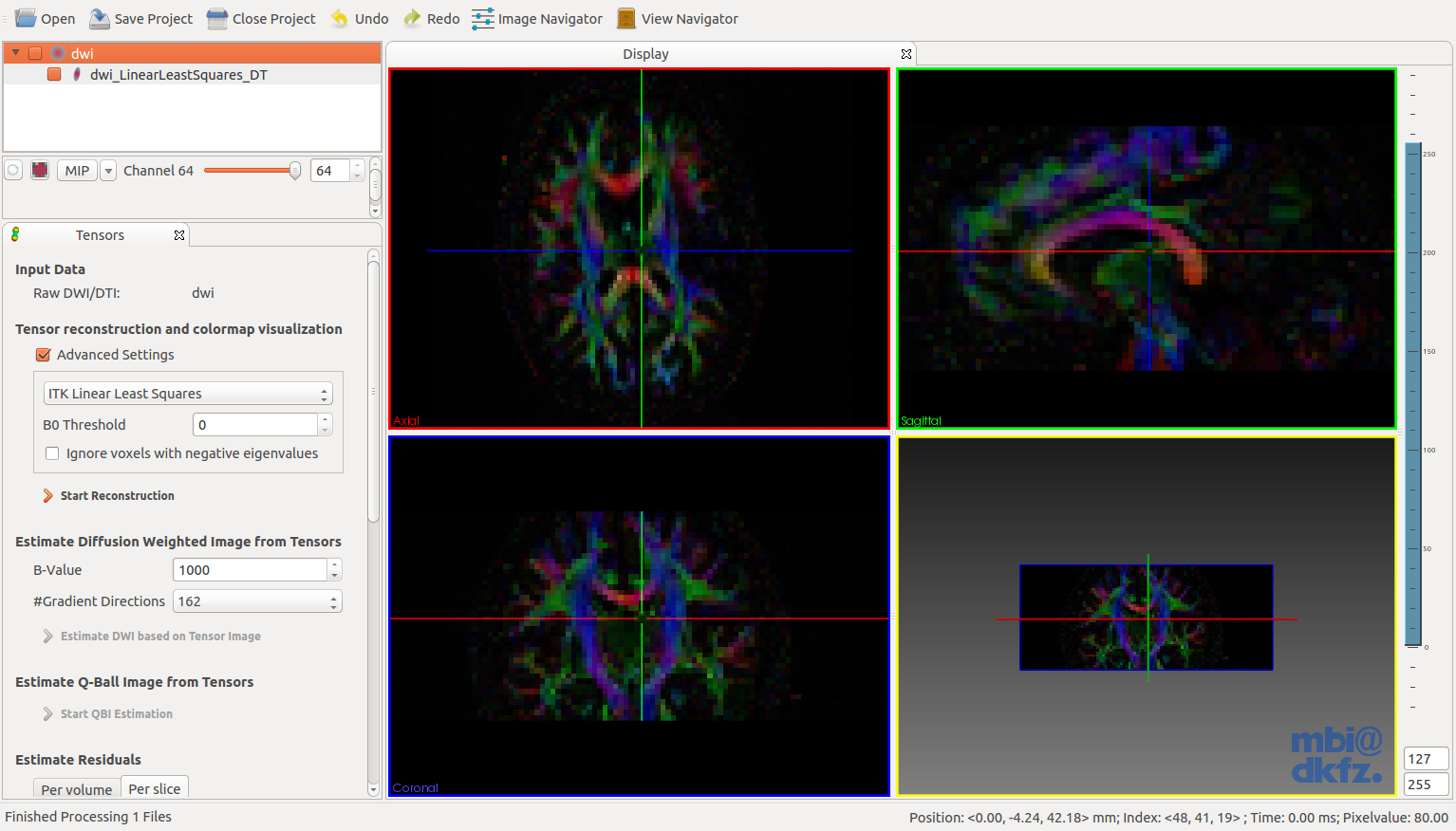
A few seconds (depending on the image size) after the reconstruction button is hit, a colored image should appear in the main window.
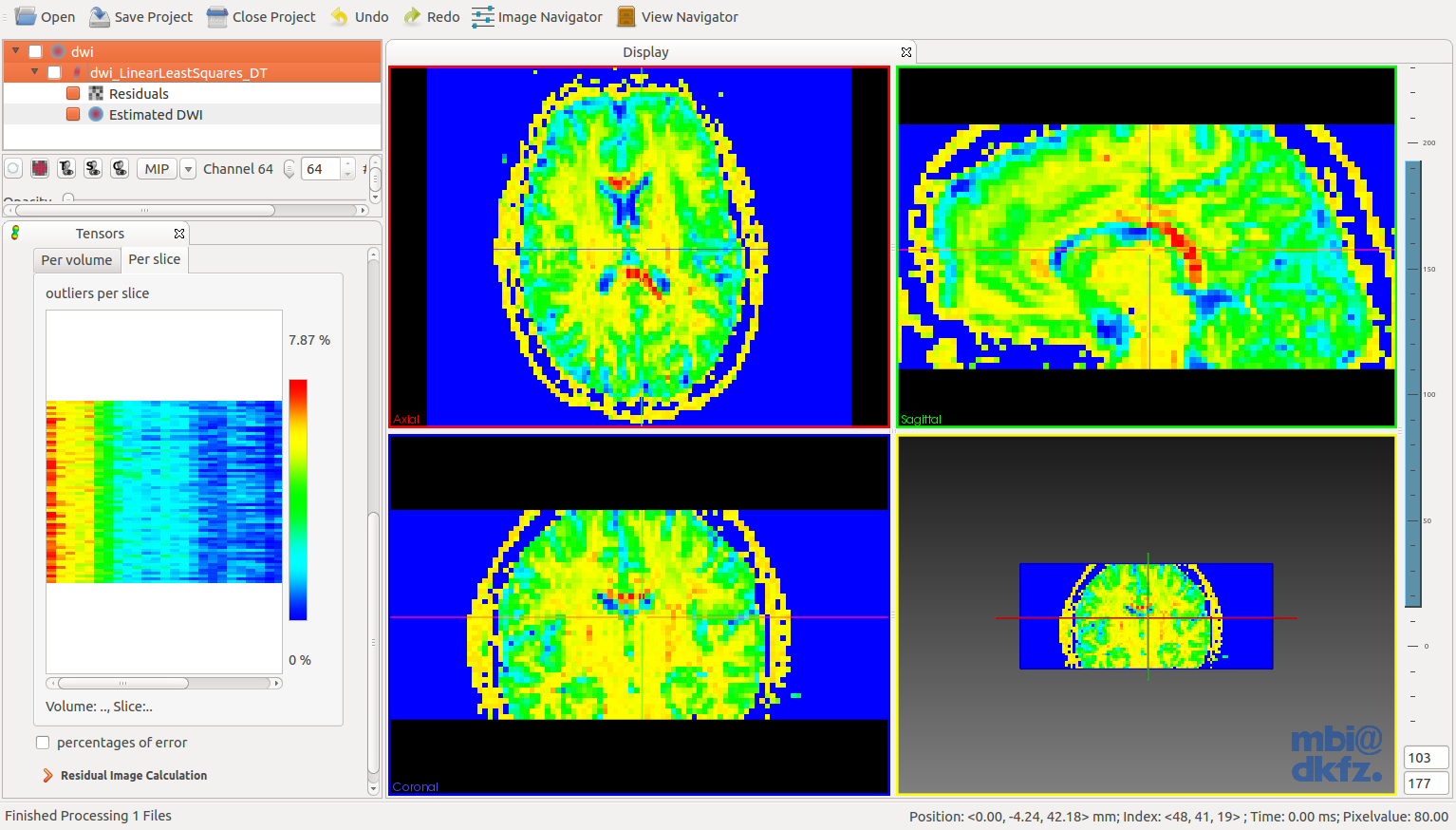
To assess the quality of the tensor fit it has been proposed to calculate the model residual [9]. This calculates the residual between the measured signal and the signal predicted by the model. Large residuals indicate an inadequacy of the model or the presence of artefacts in the signal intensity (noise, head motion, etc.). To use this option: Select a DWI dataset, estimate a tensor, select both the DWI node and the tensor node in the datamanager and press Residual Image Calculation. MITK-Diffusion can show the residual for every voxel averaged over all volumes or (in the plot widget) summarized per volume or for every slice in every volume. Clicking in the widget where the residual is shown per slice will automatically let the cross-hair jump to that position in the DWI dataset. If Percentage of outliers is checked, the per volume plot will show the percentage of outliers per volume. Otherwise it will show the mean together with the first and third quantile of residuals. See [9] for more information.
The view also allows the generation of artificial diffusion weighted or Q-Ball images from the selected tensor image. The ODFs of the Q-Ball image are directly initialized from the tensor values and afterwards normalized. The diffusion weighted image is estimated using the l2-norm image of the tensor image as B0. The gradient images are afterwards generated using the standard tensor equation.
The q-ball reonstruction view implements a variety of reconstruction methods. The different reconstruction methods are described in the following:
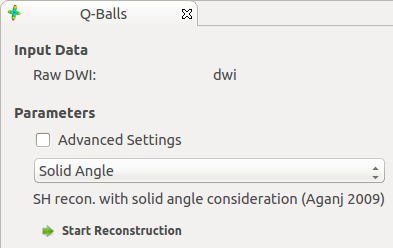
B0 threshold works the same as in tensor reconstruction. The maximum l-level configures the size of the spherical harmonics basis. Larger l-values (e.g. l=8) allow higher levels of detail, lower levels are more stable against noise (e.g. l=4). Lambda is a regularisation parameter. Set it to 0 for no regularisation. lambda = 0.006 has proven to be a stable choice under various settings.
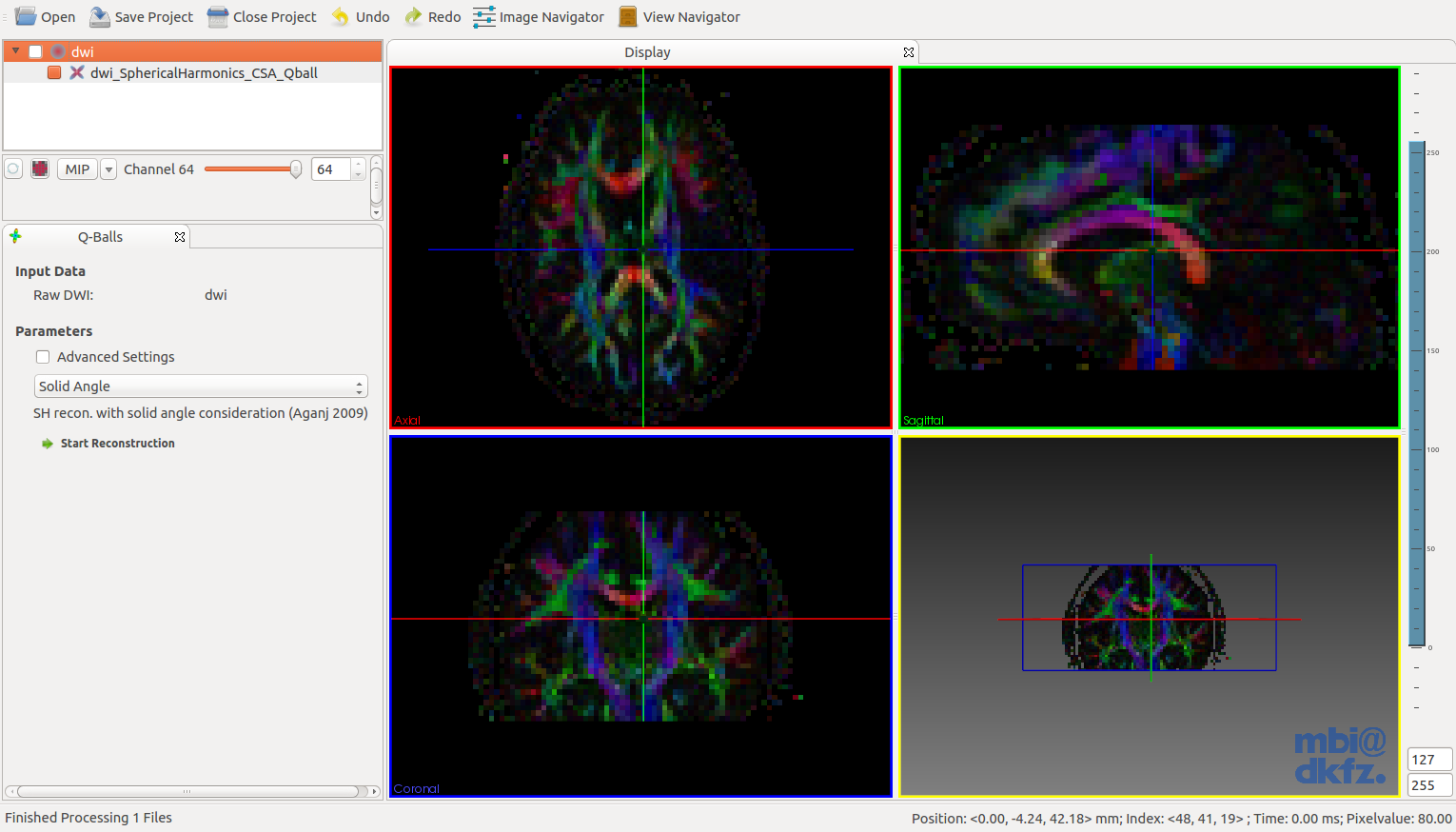
This is how a q-ball image should initially look after reconstruction. Standard q-balls feature a relatively low GFA and thus appear rather dark. Adjust the level-window to solve this.