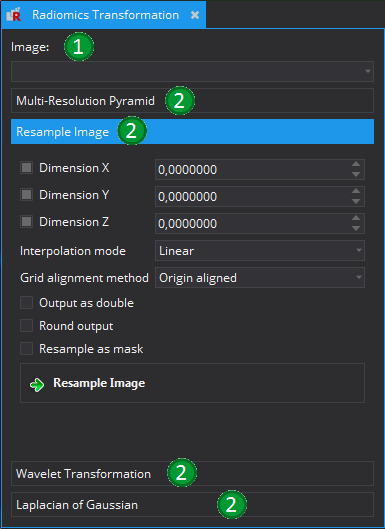
This view can be used to apply various transformation to an image. Currently it is possible to apply one of four transformations. In order to do this, a first step is to select an image (1). After this, one of the four possible transformations must be selected (2). Possible actions are:
- Multi-Reolution Pyramid
- Resample Image
- Wavelet Transformation
- Lapalcian of Gaussian
Multi-Resolution Pyramid
Creates a multi-resolution pyramid by filtering the images using a gaussian kernel and then reduing the resolution by a factor 2 for each step of the pyramid. The spacing is adapted duringt the creation of each step. Therefore, the spacial size of the image will be kept.
The view offers two possible parameters. With option (1), "Number of Levels" the number of pyramid levels are controlled. The image of the first level has always the same resolution as the input image. If the input image has 256x256 voxels in two dimensions and the number of levels is set to 4, the resulting output images will be:
- Image 0 : Resolution 256x256
- Image 1 : Resolution 128x128
- Image 2 : Resolution 64x64
- Image 3 : Resolution 32x32
With the second option (2), it is possible to ensure that the output will be of the type "double". If this option is not checked, the result will be of the same type as the input image. Beware that this might lead to some artefacts due to the resmapling artefacts.
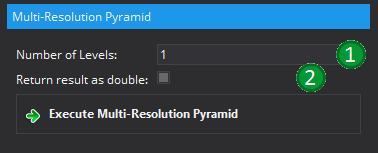
Image Resampling
Allows to simply resampling an existing image. It is based on the functionality of the MatchPoint Framework.
Options:
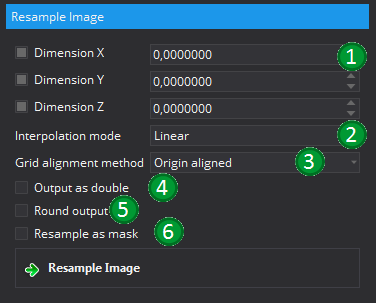
- Dimension ... (1) : The new target spacing. If this is not enabled (by deselecting the corrsponding option), or set to a negative or zero value, the original spacing will be kept and the corresponding dimension will not be resampled.
- Interpolation mode (2): Set the mode for the interpolation. Possible options are "linear" e.g. using a linear model to determine the new intensity value, "B-Spline" e.g. using a higher-dimensional function (second order), "Nearest Neighbour" e.g. using the intensity of the nearest original voxel, "WSinc Hamming", "WSinc Welch" e.g. using Hamming or Welch windowing function.
- Grid alignment method (3): Allows to define the alignment method for the newly created image. It is either "Origin algined" e.g. the origin of the original and resampled image match, "Center aligned" e.g. the center of the images are matched or "same size" in which case the resolution will be slightly adated so that the new created image will have the exact same spacial dimensions.
- Output as double (4): Returns the resampled image as double output. Without selecting this option, the resulting image will be of the same datatype as the input image.
- Round output (5): If this option is selected, the intensity values of the resampled image will be rounded to the next integer.
- Resample as mask (6): Resamples the input as mask. Assumes that the input image is a mask, but will also work with other image types. The output value is either 0 or 1. If a interpolation method other than "nearest Neighbour" is chosen, the image will be thresholded with the value 0.5 in order to create the mask.
Wavelet Transformations
Applying wavelet transformations to the original image. It is expected that the user has sufficient knowledge about Wavelet transformations if this toolbox is used.
Laplacian of Gaussian
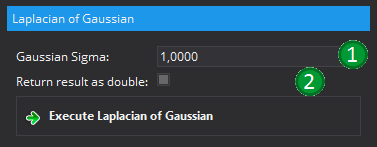
Applies a Laplacian of Gaussian Transformation to the input image. This is defined as the second order deviation of a gaussian smoothed image. The option "Gaussian Sigma" (1) defines the width of the gaussian kernel that is used by defining the corresponding sigma level in mm. It is possible to capture different details on the image by using various sigma levels.
The option "Return result as double" allows to ensure that the result will be of type double. If this option is not selected, the resulting image will be of the same type as the input image. Be aware that all calculations will be performed using the output image data type. If this is not a floating point type, the result might be affected by rounding errors.