Table of Contents
- General Changes
- How to adapt your code
- Variables are private.
- Always use PlaneGeometry instead of Geometry2D.
- Rename Geometry2D... classes.
- In some cases, use BaseGeometry instead of Geometry3D.
- Clones of BaseGeometry.
- Create an object of BaseGeometry.
- Virtual functions.
- Parametric functions are not part of BaseGeometry.
- There is no float spacing any more.
- Always use LandmarkProjectorBasedCurvedGeometry instead of LandmarkBasedCurvedGeometry.
General Changes
Old class diagram
Until now, all geometry classes inherited from Geometry3D. This inheritance didn't make sense. For example, there is no reason, why we need a Geometry2D and a PlaneGeometry as both describe the same thing. Also, why does a two-dimensional class need to inherit from a three-dimensional class?

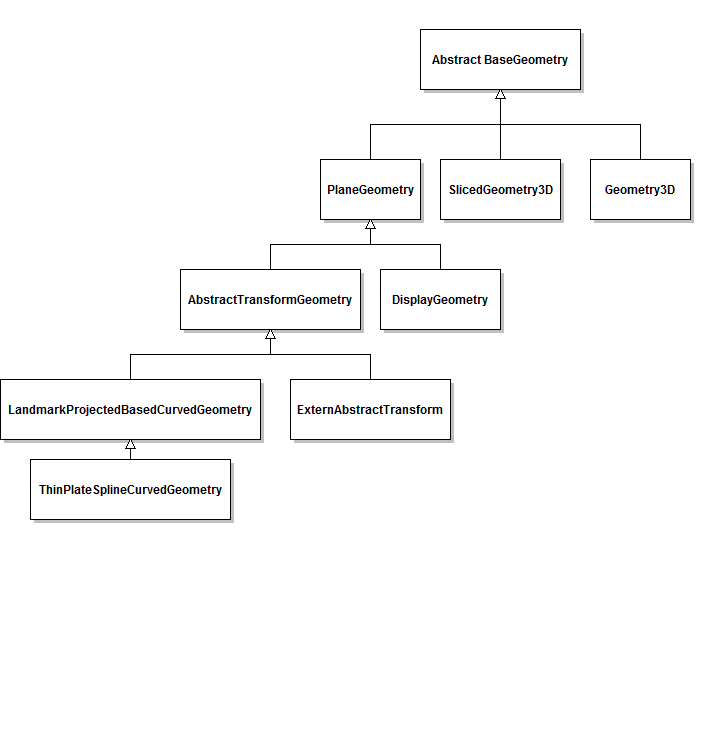
New class diagram
Therefore, we inserted an abstract BaseGeometry class, from which all other geometry classes should inherit. The classes Geometry2D and PlaneGeometry are combined in the new PlaneGeometry class. Also, the LandmarkBasedCurvedGeometry is included in LandmarkProjectorBasedCurvedGeometry.
How to adapt your code
Most content of the BaseGeometry class consists of functions and variables of the former Geometry3D. Here are some guidelines, how to change your code to the new geometry scheme.
Variables are private.
All variables of BaseGeometry (former in Geometry3D) are private now. Hence, use the Set and Get methods to access the variables.
Always use PlaneGeometry instead of Geometry2D.
The class Geometry2D does not exist any more. In most cases, you can just replace the Geometry2D by PlaneGeometry. Please pay attention if you use the function "IsAbove(Point3D point)". There were two different implementations in Geometry2D and PlaneGeometry. The default behavior is implemented according to the former function of PlaneGeometry. If you want to use the implementation of the former Geometry2D, please call "IsAbove(point,true)".
Here are the different implementations:
Rename Geometry2D... classes.
All ...Geometry2D... classes and functions are renamed to ...PlaneGeometry... . The new names are for example PlaneGeometryData instead of Geometry2DData. An example for functions is GetGeometry2D, which is now called GetPlaneGeometry. A simple search & replace of Geometry2D should work in most cases.
List of all names changed (excluding variables):
- Geometry2D
- Geometry2DData
- Geometry2DDataToSurfaceFilter
- Geometry2DDataMapper2D
- Geometry2DDataVTKMapper
- GetCurrentWorldGeometry2D
- GetCurrentWorldGeometry2DNode
- GetCurrentWorldGeometry2DUpdateTime
- SetCurrentWorldGeometry2D
- GetGeometry2DData
- GetGeometry2D
- SetGeometry2D
In some cases, use BaseGeometry instead of Geometry3D.
As there are no classes any more, which inherit from Geometry3D, you cannot insert other classes (i.e. SlicedGeometry3D) for a Geometry3D. If you have trouble, e.g. calling a function which expects a Geometry3D parameter, try one of the following steps:
- Do you really need a Geometry3D? Maybe you always use e.g. a PlaneGeometry. Change your function to PlaneGeometry.
- If your function/object needs to be flexible for all geometry classes, change the Geometry3D to BaseGeometry.
- Try dynamic type casts to BaseGeometry.
Clones of BaseGeometry.
The BaseGeometry class is an abstract class. You cannot create an object of BaseGeometry. If you need a clone of BaseGeometry to call a function, use the following code:
instead of:
Create an object of BaseGeometry.
Again, you cannot create an object of BaseGeometry. However, there are cases, where we need a flexible Variable which can contain objects of any other geometry class later on. This might be the case for member variables, etc. In this case, try:
instead of
Virtual functions.
To ensure a reliable behavior of functions, most functions are not virtual any more. However, if a function needs a different behavior in subclasses, there are virtual Pre- and Post- functions, which allow for additional code. The pre-functions are called at the very beginning of a function, the post-functions at the end. In the BaseGeometry, all pre- and post-functions are empty.
An example:
The function "SetIndexToWorldTransform" is not virtual any more. For a PlaneGeometry, we need a perpendicular normal before the transformation is set. Afterwards, we need to apply the transformation to the scaling factors.
Code of the BaseGeometry class:
Code of PlaneGeometry:
Parametric functions are not part of BaseGeometry.
In Geometry3D, there were several "Parametric" functions (e.g. GetParametricExtent, GetParametricTransform), which only called the non-parametric function (e.g. GetExtent, GetIndexToWorldTransform). These functions are removed, please use the non-parametric implementation instead. However, in the AbstractTransformGeometry (and all subclasses), these parametric functions behave different and are still available.
There is no float spacing any more.
Use GetSpacing instead of GetFloatSpacing.
Always use LandmarkProjectorBasedCurvedGeometry instead of LandmarkBasedCurvedGeometry.
The class LandmarkBasedCurvedGeometry does not exist any more. Please use LandmarkProjectorBasedCurvedGeometry.
